Traction Gas Springs
Traction gas springs with threads
We’ll usually dispatch your order the same day with expected delivery within 2-4 days. This applies to all stocked traction gas springs.
See quantity discounts and prices by clicking on the shopping cart next to the required product.
Use the range sliders below for quick and easy navigation.
The function of a traction gas spring is the opposite of conventional compression gas springs. The piston rod is in an unloaded state inside the cylinder. When the piston rod is loaded and pulled out, the force will attempt to pull the piston back into the cylinder again.
The cylinder on the traction gas spring is painted black. The piston rod is treated with nitrides to provide moderate rust protection. However, we do not recommend that these traction gas springs be used in a humid environment.
Our stainless steel gas springs are only available in the best quality. Traction gas springs can be used in the food industry, as they can withstand harsh cleaning agents. At the same time, food-grade (FDA) oil (Omnilube FGH 1046) has been used in our stainless steel traction gas springs.
The piston rod does not need to be lubricated and is maintenance-free. If the gas spring is to be used in a dirty environment, it can be protected with a rubber bellows. Read more
23-70024-description
Stainless steel 316
23-70021-description
Black painted steel
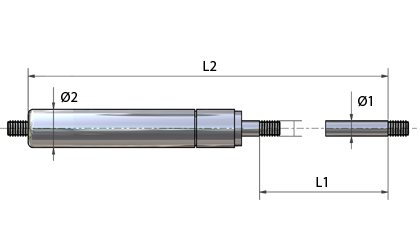
- TGF-8-20-100In stock: 129Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 22.4809L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-100-316In stock: 93Material Stainless steel 316Ø1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 22.4809L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-100-TIn stock: 0Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 22.4809L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-150In stock: 149Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 33.7213L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-150-316In stock: 95Material Stainless steel 316Ø1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 33.7213L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-150-TIn stock: 0Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 33.7213L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-200In stock: 149Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 44.9618L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-200-316In stock: 95Material Stainless steel 316Ø1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 44.9618L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-200-TIn stock: 0Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 44.9618L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
- TGF-8-20-250In stock: 151Material Black painted steelØ1 - Piston Rod diameter (in) 0.3150Ø2 - Tube diameter (in) 0.8661L1 - Stroke (in) 0.7874F - Force (lbs) 56.2022L2 - Unloaded length between thread (in) 3.9370G - Thread (in) 0.2362K - Force ratio 1.3000
Cylinder: Welded cold-formed pipe EN 10305-3 ST37 / S14
Piston Rod: C35R . The cylinder is painted semi-matte black, and the piston rod has been given a plasma nitride treatment that makes the surface extremely hardwearing and provides moderate rust protection. However, the treatment cannot replace a dedicated stainless steel gas spring.
Oil: The oil is a common lubrication oil, but is not approved for food use.
Gas: Nitrogen N2 Std.
Atmospheric air contains 78.09% nitrogen and is the basis for the production of nitrogen by means of distillation of liquid air.
Nitrogen is odourless, colourless, non-toxic, and non-flammable.
Cylinder & piston rod: Stainless steel gas springs are made from AISI 316 stainless steel.
Oil: The oil is approved for food use. (Omnilube FGH 1046)
Gas: Nitrogen N2 Std.
Atmospheric air contains 78.09% nitrogen and is the basis for the production of nitrogen by means of distillation of liquid air.
Nitrogen is odourless, colourless, non-toxic, and non-flammable.
Total length (L2): +/- 0.01181 "
Stroke (L1): +/- 0.0788 "
Max force (Fn): +/- 10 %
Gas springs contain nitrogen gas under high pressure. This is a type of gas that cannot burn or explode, nor is it toxic if inhaled. No attempt must be made, in any circumstances, to take the gas spring apart or to refill it - this is extremely risky due to the high pressure! Do not burn, puncture, squash or dent the gas spring, and do not weld the surface of the cylinder. Do not scratch, paint or bend the piston.
Never use gas springs as a safety device. If damage to a gas spring could result in personal injury, provision must be made for this by means of a safety device. If any construction incorporating a gas spring could cause personal injury in the event of loss of gas from the spring, an additional safety device must be used to prevent injury. In some constructions, locking tubes for gas springs can be used. This safeguards the construction in the event of a sudden pressure drop in the gas spring.
No need to lubricate the piston rod, as the range of gas springs is maintenance-free.
Gas springs are filled at 68°F, and the initial force is therefore measured at 68°F.
The force will change by approximately 3-3.5% per 50°F. The colder it is, the weaker the gas spring becomes. Our gas springs work best in temperatures between -22°F and +176°F. Using the springs in temperatures close to those limits will produce an altered force, and maximal usage cannot be recommended.
Traction gas springs contain a special kind of grease as a lubricant instead of oil. This kind of lubricant ensures that seals, etc. stay lubricated during storage and when fitted at any angle. Traction gas springs have no damping. However, we recommend fitting the traction gas spring with its piston facing upwards.
Gas springs are designed to perform no more than 5 strokes per minute at 68°F. If this is exceeded, there will be a build-up of heat inside the gas spring that may result in leaky glands.
Gas springs will lose pressure slightly over time, compared with the original pressure at the time they were fitted. A pressure loss of up to 10% may be expected.
Always use the shortest possible travel, and choose the largest possible diameter on the cylinder - this increases the durability. Long and thin gas springs will be weaker than short and wide gas springs.
If you want a PDF datasheet or a 3D CAD drawing of the spring in .step, .iges or .sat format, these can be downloaded for free by clicking on the 3D CAD symbol next to the item number in the table.